Symptoms and Diagnosis of UTIs
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is usually caused by bacteria, but fungi and viruses may also lead to such an infection. UTIs are the most commonly occurring infections, so one should understand the condition and its symptoms. Identifying the early symptoms can help treat a UTI at the earliest. This article looks at some of the common symptoms of UTI and its diagnosis.
1. Symptoms of a UTI
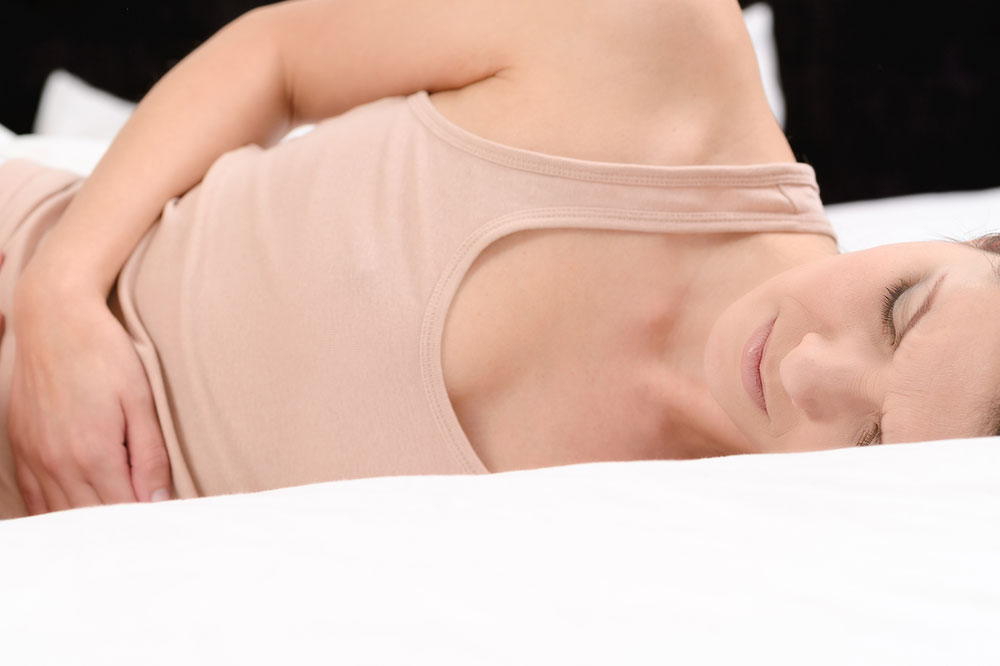
In a well-hydrated, healthy person, urine mostly appears clear or light yellow and free of odor, and one does not experience any pain or discomfort while urinating. In contrast, people who contract a UTI may experience the following symptoms:
- Frequent and strong urges to urinate
Bacteria cause the bladder and urethra to swell and get irritated in people with a UTI, triggering frequent urges to pee. - A burning sensation or pain while urinating
Bacteria can irritate the urinary tract’s lining and result in inflammation. This might cause pain or an unpleasant sensation while passing urine. - Inability to empty the bladder
A UTI may cause an individual to visit the bathroom frequently, but one might be able to pass only a small amount of urine in one go. This also leads patients to feel as if the bladder has not been emptied. - Cloudy and foul-smelling urine
There is cloudiness in the urine because of the buildup of white blood cells when the body tries to combat the bacteria that cause UTIs. Bacteria can also make the urine smell. - Dark-colored urine
A dark color is an indication of the presence of blood in the urine. - Pelvic pain or pressure
The pressure associated with a UTI generally develops in the middle of the pelvis and might feel like bloating. - Passing gas while urinating
This is known as pneumaturia and results from gas in the urinary tract. - Pus-like urethral discharge
This is a more common symptom of UTIs in men than in women, and it occurs as the bladder and urethra’s mucus attempts to rid the body of pathogens. - Incontinence
UTI might also weaken the bladder muscles and cause a lack of bladder control. This is more common in older people and can lead to incontinence.
2. Diagnosis of a UTI
Some of the diagnostic procedures and tests for UTI are:
- Examining the urine sample
Firstly, the doctor may ask for a urine sample to check for bacteria, white blood cells, or red blood cells. Patients might be asked to wipe the genital area using an antiseptic pad before collecting a sample to prevent its contamination. - Urine culture
If one shows the symptoms of a UTI, they might have to undergo a urine culture for diagnosis and to help the doctor to know what bacteria has caused it. - Ultrasound, CT, and MRI
A doctor may recommend MRI, CT scan, and ultrasound to check for irregularities or abnormalities if one frequently contracts UTIs.